Data Science and Big Data: Unveiling the Secrets
- Oct 1, 2023
- 2 min read
Introduction: In our data-driven age, information is the new currency, and those who can extract meaning from the deluge of data hold the key to innovation and success. Data Science and Big Data are the twin pillars of this digital revolution, allowing us to unravel patterns, make predictions, and uncover hidden treasures within vast datasets.

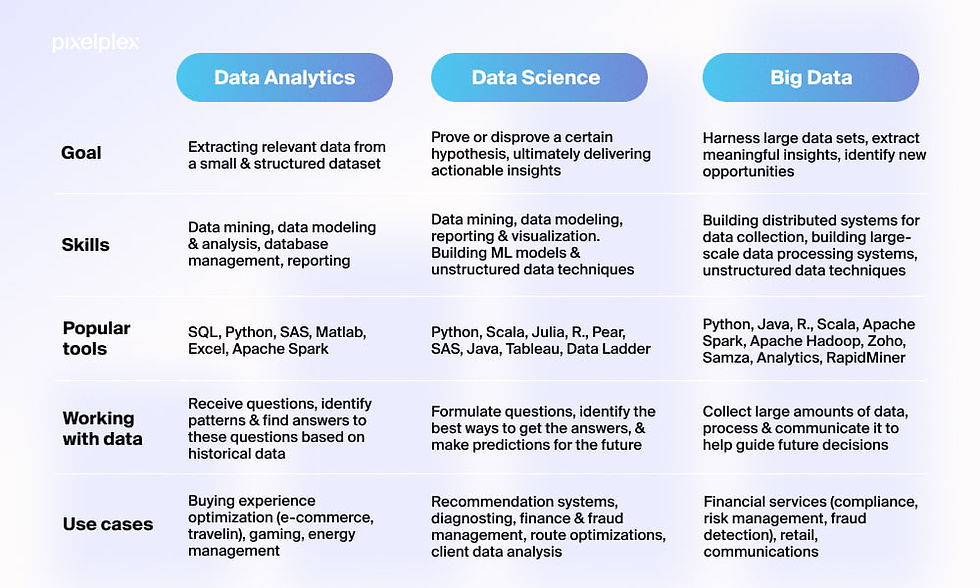
Data Science: The Art of Insight:
1. Data Collection and Cleaning:
Collection: Data scientists gather data from various sources, such as databases, sensors, and web APIs.
Cleaning: Raw data is often messy, so cleaning involves handling missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies.
2. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA):
Data scientists explore data through visualization and statistical analysis to gain a deeper understanding of its characteristics.
3. Machine Learning Models:
Data scientists employ machine learning algorithms to build predictive models.
Examples include classification models for spam email detection or regression models for price prediction.
4 . Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP techniques enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Chatbots and sentiment analysis are real-world applications of NLP.

Big Data: Handling the Data Deluge:
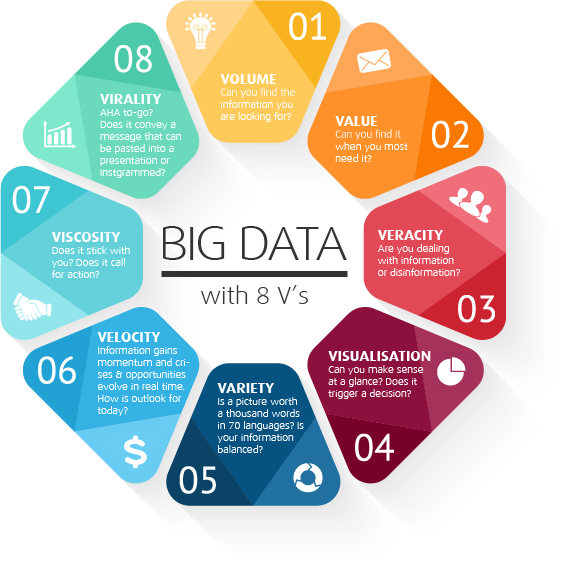
1. Volume, Velocity, Variety, and Veracity:
Big Data is characterized by the "Four Vs": Volume (large datasets), Velocity (fast data streaming), Variety (varied data types), and Veracity (uncertainty in data quality).
2. Distributed Computing:
Big Data processing often requires distributed computing frameworks like Hadoop and Spark to handle immense datasets efficiently.
Real-World Examples:
1. Netflix Recommendations:
Netflix uses data science to recommend movies and shows based on user viewing history, preferences, and ratings.
This personalized recommendation system keeps users engaged and drives subscriptions.
2. Healthcare Predictive Analytics:
Hospitals employ data science to predict patient readmission rates, enabling early interventions and cost savings.
Predictive models can identify patients at risk of chronic diseases, improving patient care.
3. E-commerce Product Recommendations:
Amazon and other e-commerce giants use data science to suggest products to customers based on their browsing and purchase history.
This leads to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
4. Weather Forecasting:
Meteorologists use Big Data and advanced modeling to make accurate weather predictions.
This is critical for disaster preparedness and agriculture planning.
5. Social Media Sentiment Analysis:
Companies monitor social media sentiment to understand customer opinions and brand perception.
This feedback helps in product development and marketing strategies.
Challenges and Future Trends:
1. Ethical Considerations:
Ensuring privacy and ethical use of data remains a top concern.
2. AI Integration:
The integration of AI and machine learning with Big Data analytics will lead to more advanced and automated insights.
3. Real-time Analytics:
The demand for real-time data processing and analysis will continue to grow.
4. Edge Computing:
Processing data closer to its source (edge devices) will reduce latency and improve efficiency in IoT and other applications.
In conclusion, Data Science and Big Data are transforming industries and reshaping how we make decisions. They are not just fields; they are tools that enable businesses and organizations to innovate, optimize operations, and improve the quality of life. As we move forward in this data-driven era, the possibilities are endless, and those who harness the power of data will lead the way into the future.




Comments